Abstract
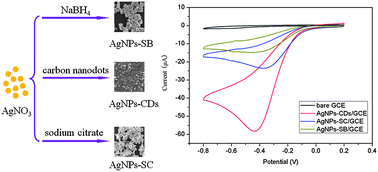
Nitrogen-doped carbon nanodots (CDs) were found to possess reductive activity and could catalytically reduce AgNO3 to produce Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs). The AgNPs reduced by CDs (AgNPs-CDs) exhibit better catalytic activity toward electrochemical reduction of H2O2than that of AgNPs reduced by NaBH4 (AgNPs-SB) and sodium citrate (AgNPs-SC), leading to a high-performance non-enzymatic H2O2 sensor. The linear detection range is estimated to be from 0.1 mM to 60 mM (r = 0.999), and the detection limit is estimated to be 0.5 μM at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3.